Cell references are a fundamental concept in Microsoft Excel, allowing users to refer to specific cells or ranges in formulas. By understanding and using cell references effectively, you can create dynamic and flexible spreadsheets. This tutorial explains the types of cell references in Excel—Relative, Absolute, and Mixed—along with detailed examples to demonstrate their application.
What Are Cell References?
In Excel, a cell reference identifies the location of a cell or a range of cells in a worksheet. For example, A1 refers to the cell at the intersection of column A and row 1. Cell references are used in formulas to perform calculations based on the data in those cells. Excel provides three types of cell references:
Types of Cell References in Excel
There are two types of cell references in Excel:
- Relative reference
- Absolute reference
Relative Reference in Excel
Relative reference is the default cell reference in Excel. It is simply the combination of column name and row number without any dollar ($) sign. When you copy the formula from one cell to another the relative cell address changes depending on the relative position of column and row. C1, D2, E4, etc are examples of relative cell references. Relative references are used when we want to perform a similar operation on multiple cells and the formula must change according to the relative address of column and row.
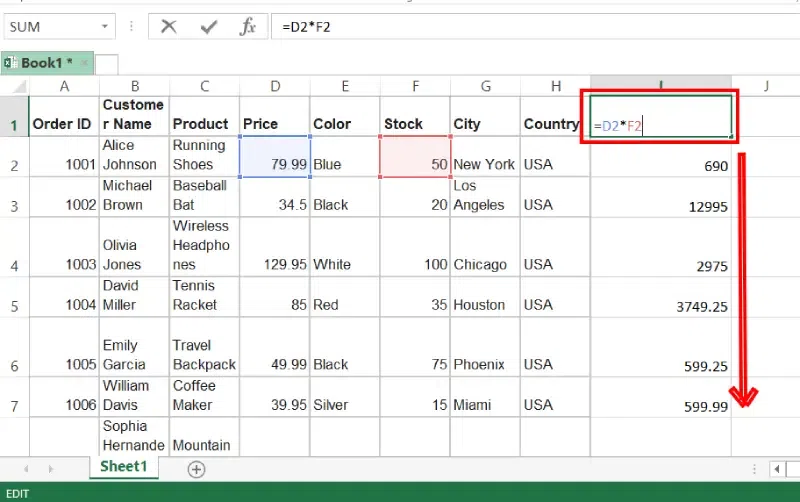
Absolute Reference in Excel
An absolute reference is the cell reference in which the row and column are made constant by adding the dollar ($) sign before the column name and row number. The absolute reference does not change as you copy the formula from one cell to another. If either the row or the column is made constant then it is known as a mixed reference. You can also press the F4 key to make any cell reference constant. $A$1, $B$3 are examples of absolute cell reference.
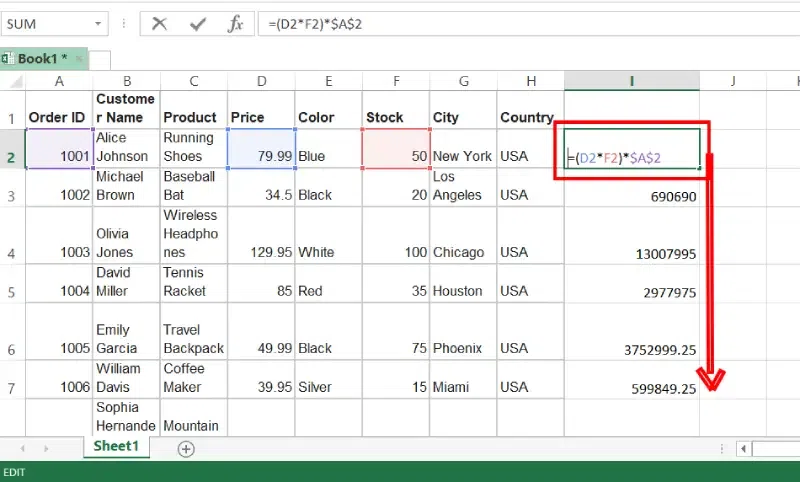
How to Use Excel’s Relative Reference – Example
We want to add the marks of two subjects entered in column A and column B and display the result in column C. Here, we will use relative reference so that the same rows of columnsExcel A and B are added.
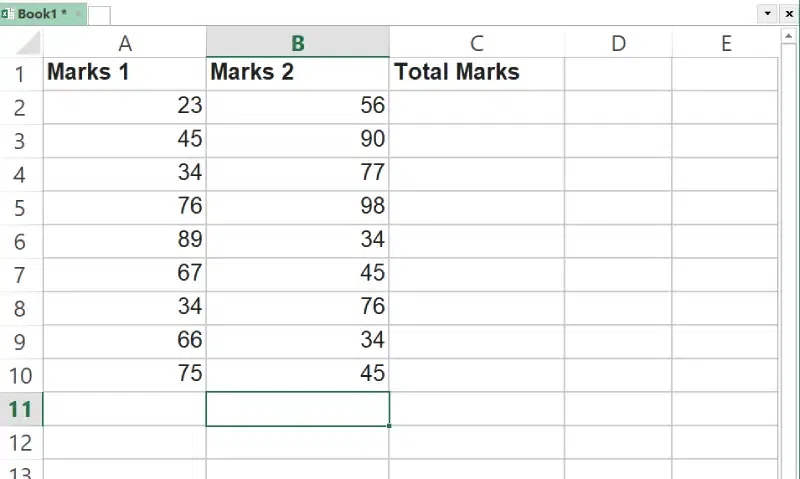
Step 1: Open Excel and Enter Data
Open your Excel Sheet and enter the data into the Excel sheet. In this example, we are entering marks 1 and 2 in columns A and B respectively with total marks in column C.
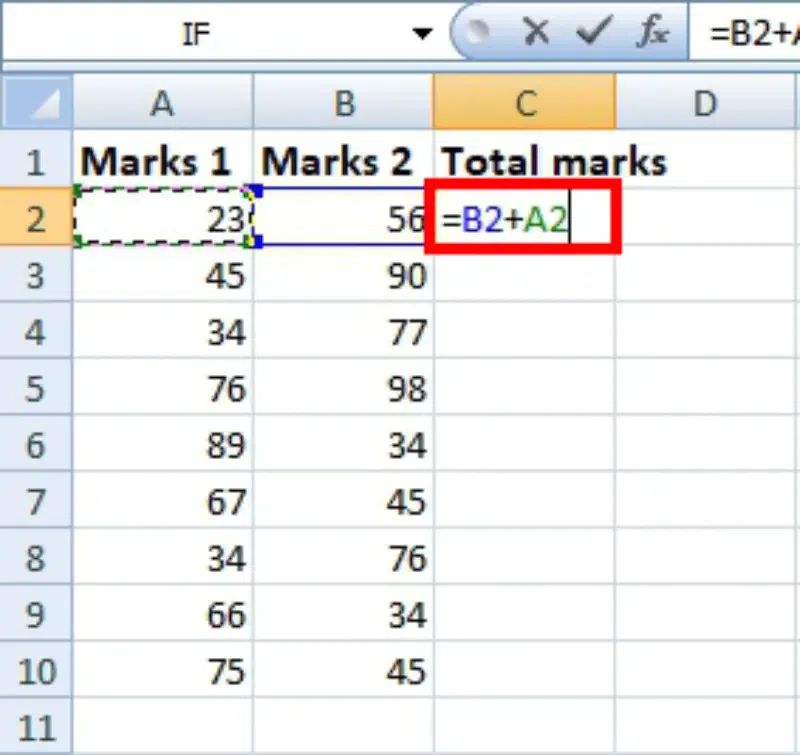
Step 2: Enter the Formula
Now we need to enter the formula to add marks 1 and 2. We write the formula in any cell and press enter so that it is calculated. In this example, we write the formula(= B2 + A2) in cell C2 and press enter to calculate the formula.
Step 3: Click on Fill Handle
Now click on the Fill handle at the corner of the cell which contains the formula(C2).
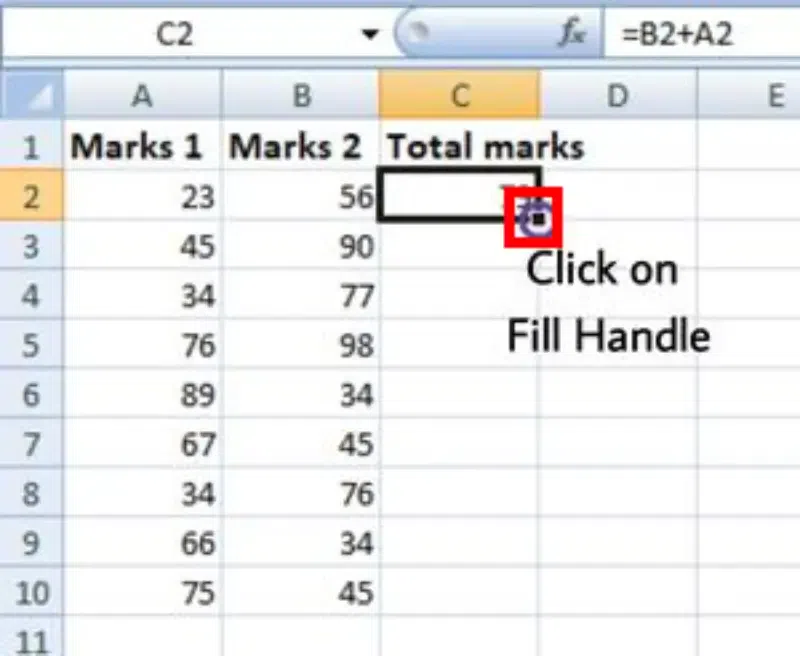
Step 4: Drag the Handle
Drag the Fill handle up to the cells you want to fill. In our example, we will drag it to cell C10.
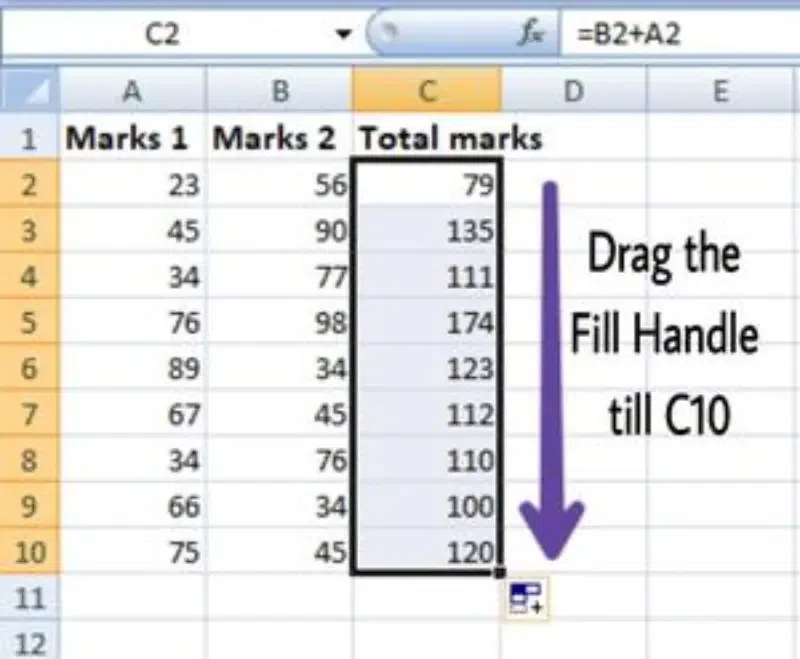
Now we can see that the addition operation is performed between the cells A2 and B2, A3 and B3, and so on.
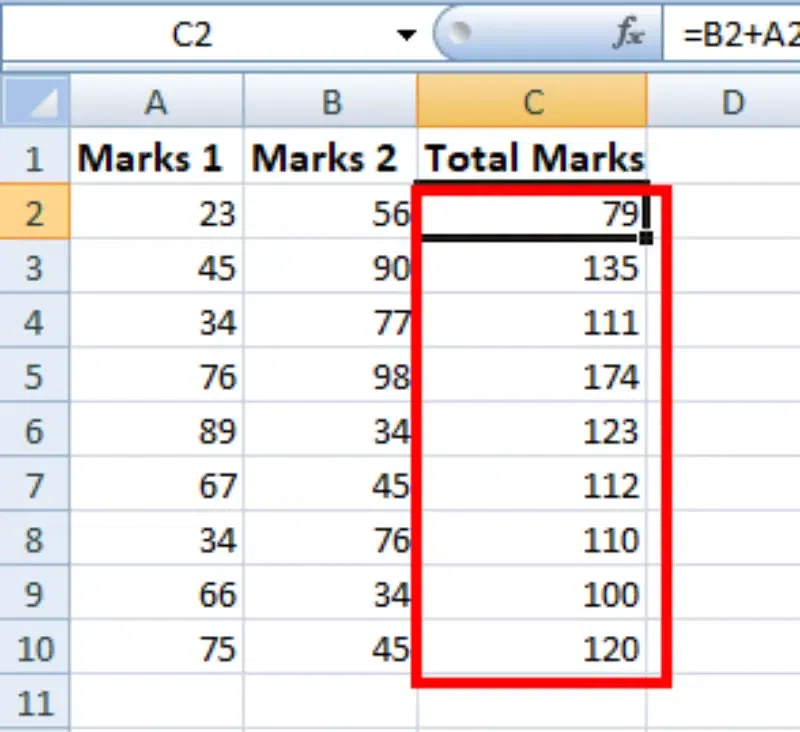
Step 5: Check the Performed Action
You can double-click on any cell to check that the operation is performed in between which cells.
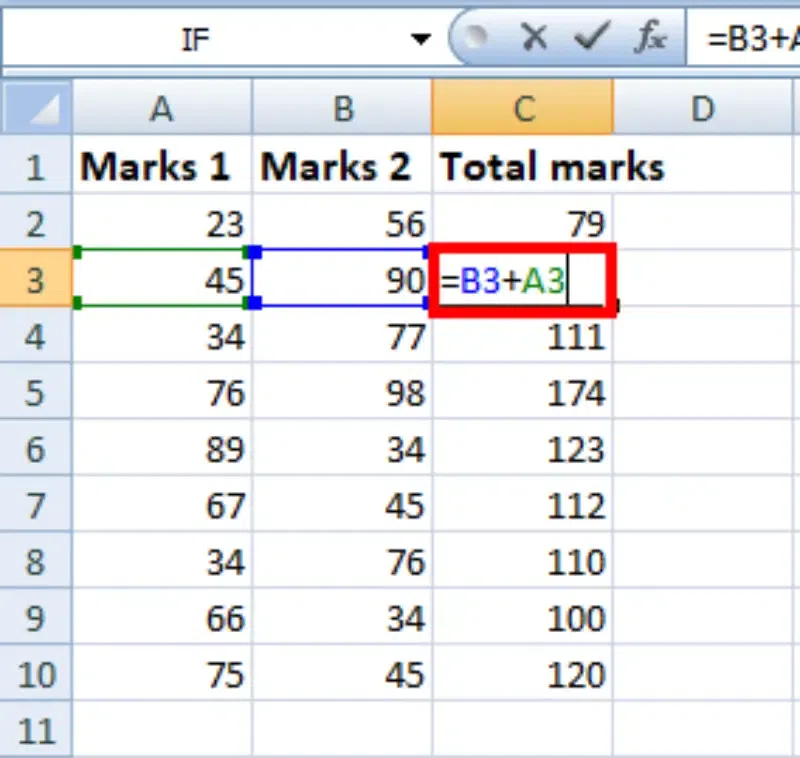
Thus, in the above example, we see that the relative address of cell A2 changes to A3, A4, and so on, similarly the relative address changes for column B, depending on the relative position of the row.
How to Use Absolute Reference: Example
For example, We want to multiply the sum of marks of two subjects, entered in column A and column B, with the percentage entered in cell C2 and display the result in column D. Here, we will use absolute reference so that the address of cell C2 remains constant and does not change with the relative position of column and rows.
Step 1: Open Excel and Enter Data
Open your Excel Sheet and enter the data into the Excel sheet. In this example, we are entering marks 1 and 2 in columns A and B respectively with total marks in column C.
Step 2: Enter the Formula
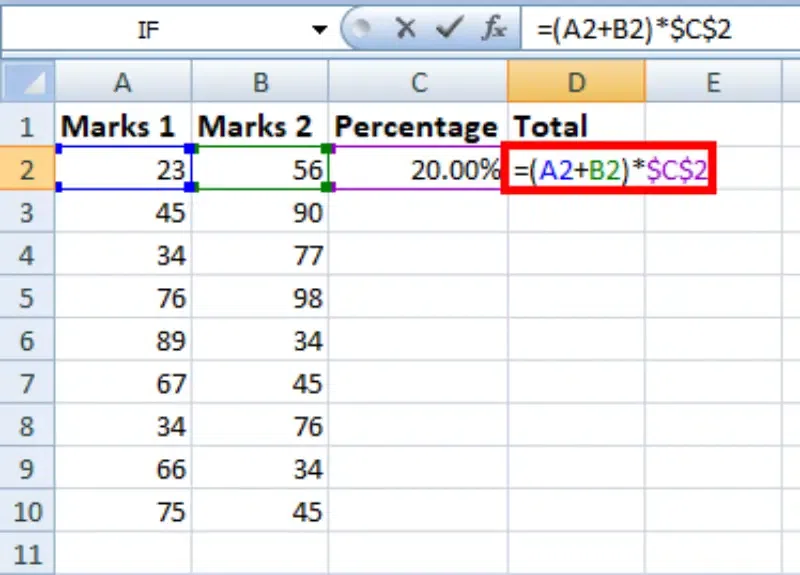
We write the formula in any cell and press enter so that it is calculated. In this example, we write the formula(=(A2+B2)*$C$2) in cell D2 and press enter to calculate the formula
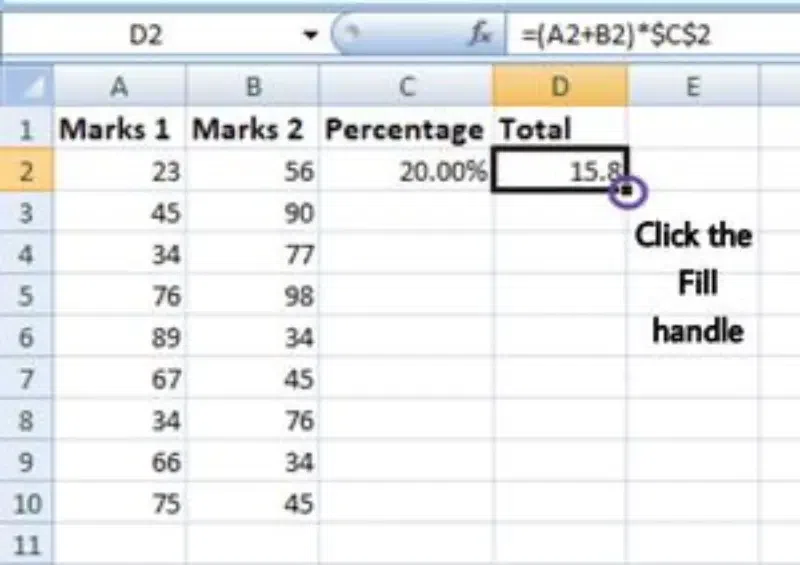
Step 3: Click on Fill Handle
Now click on the Fill handle at the corner of the cell which contains the formula(D2).
Step 4: Drag the Handle
Drag the Fill handle up to the cells you want to fill. In our example, we will drag it to cell D10.
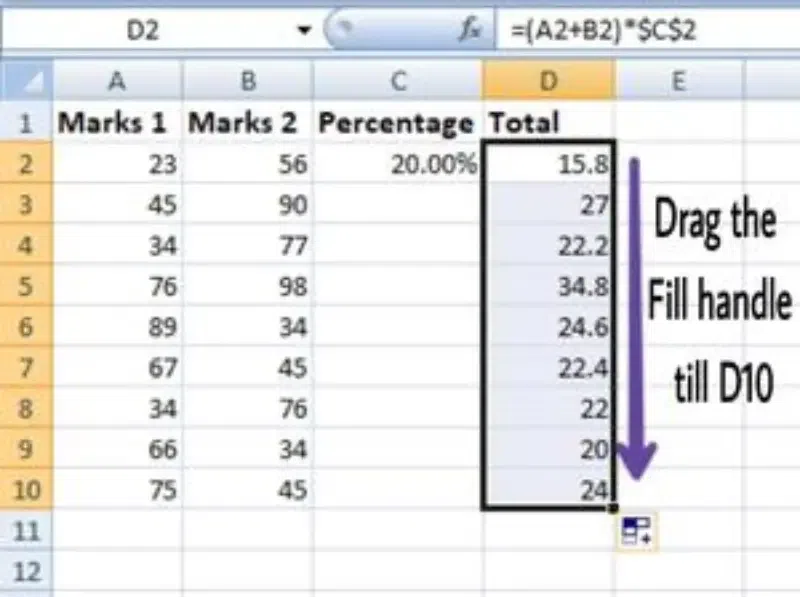
Now we can see that the percentage is calculated in column D.
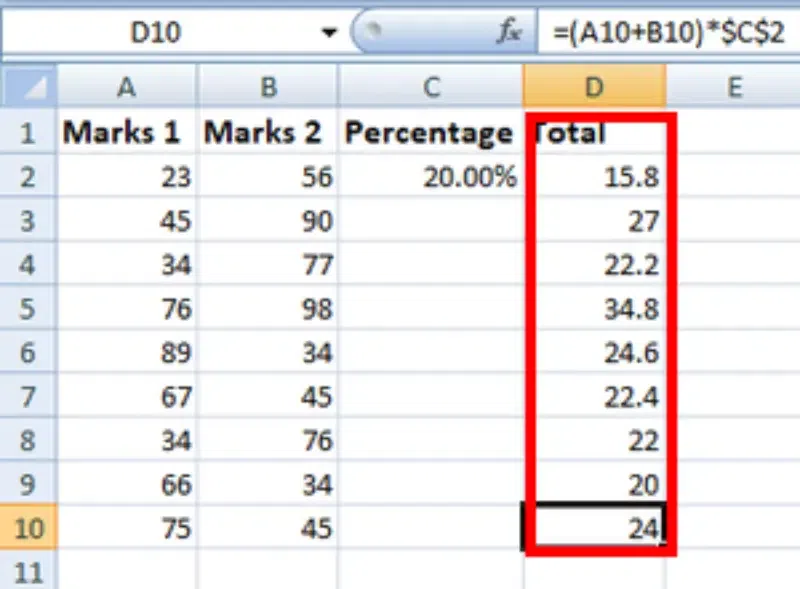
Step 5: Check the Performed Action
You can double-click on any cell to check that the operation is performed in between which cells, and we see that the address of cell C2 does not change.
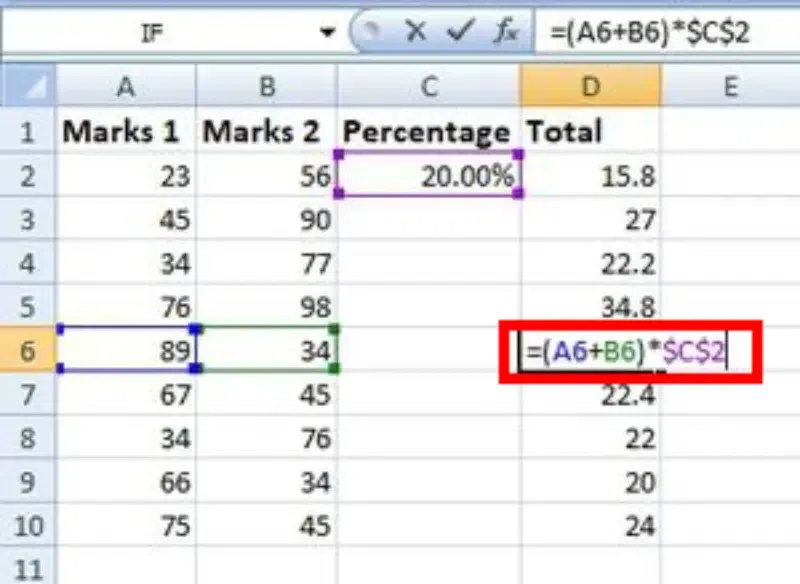
Thus, in the above example, we see that the address of cell C2 is not changed whereas the address of columns A and B changes with the relative position of the row and column, this happened because we used the absolute address of cell C2.
How to use Cell References with Multiple Worksheets in Excel
Step 1: Open Excel and Enter Data
Open your Excel Sheet and enter the data into the Excel sheet. In this example, we are entering marks 1 and 2 in columns A and B respectively with total marks in column C.
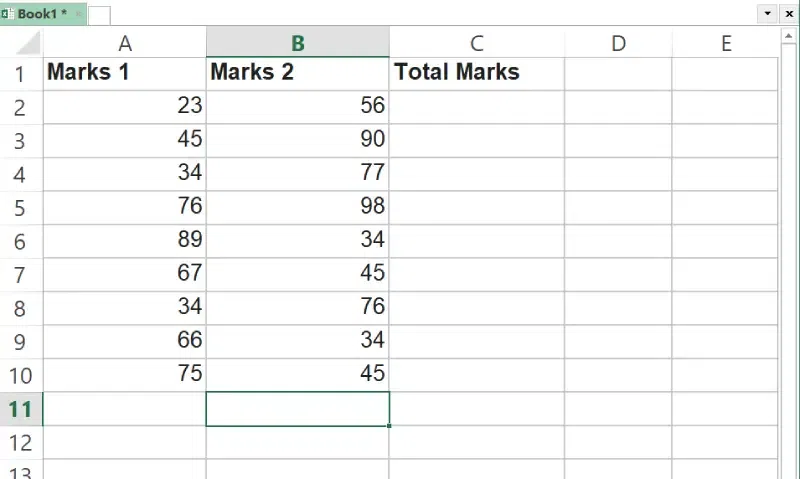
Step 2: Locate the Cell for Reference
Locate the Cell for Reference and note down its worksheet name.
Step 3: Access Second Worksheet
Go to the second worksheet of your Choice and Select it
.webp)
Step 4: Locate Cell
Go to the Cell where you want to store the value.
Step 5: Enter Equals To followed by Sheet Name and Exclamation
Enter the equal to sign in the selected cell followed by the worksheet name followed by! sign. Hit Enter.
.webp)
Difference Between Absolute and Relative cell Reference in Excel
| Aspects | Relative Reference | Absolute Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Definition |
Adjusts its location based on the relative position of the formula |
Remains constant regardless of where it is copied or filled |
| Symbol | Typically represented without any dollar signs ($) | Usually indicated by adding dollar signs ($) before column and row |
| Example | If copied from A1 to B1, it changes to B1 | Remains as $A$1 when copied or filled to other cells |
| Usage | Useful for calculations that involve moving formulas | Ideal for keeping specific cell references constant |
| Syntax | Contains only the column and row references | Contains column and row references with dollar signs ($) |
| Example Formula | =A1+B1 |
=$A$1+$B$1 |
Challenge!
- Open an existing Excel workbook. If you want, you can use the Example file for this lesson.
- Create a formula that uses a relative reference. If you are using the example, use the fill handle to fill in the formula in cells E4 through E14. Double-click a cell to see the copied formula and the relative cell references.
- Create a formula that uses an absolute reference. If you are using the example, correct the formula in cell D4 to refer only to the tax rate in cell E2 as an absolute reference, then use the fill handle to fill the formula from cells D4 to D14.
- Try referencing a cell across worksheets. If you are using the example, create a cell reference in cell B3 on the Catering Invoice worksheet for cell E15 on the Menu Order worksheet.